Description
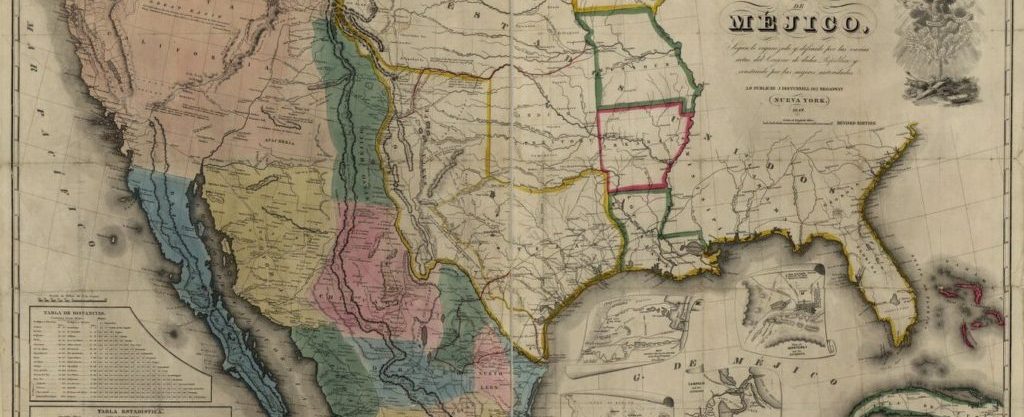
This assignment helps students think critically about the geographical and political definition of the U.S.-Mexico boundary and its effect on people living in the borderlands through the analysis of the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo text and contemporary historical maps using text visualization tools.
Date Range(s): 1735-1848
Grade Level(s): High School; Undergraduate
Country(ies): Mexico; United States
Course Subject(s): Borderland Studies; Digital Scholarship; Indigenous Studies; Latin American Studies; Linguistic & Language Studies; Literary Studies; Mexican American & U.S. Latinx Studies; U.S. History, pre-1877; World Geography Studies; World History Studies
Topic(s): Native Americans; Mapping; Politics; Property Rights
Guiding Questions
What causes a national boundary to change? How does the movement of a territory’s boundary affect the lives of people along the newly defined borderlands? How are terms used in the treaty used to define various people living along the border?
Learning Objectives
- Students will examine the reasons for and consequences of moving a national boundary on the rights and lives of citizens in both countries.
- Students will take a critical look at how both governments perceived, and their actions towards, Native populations along the U.S.-Mexico border.
- Students will examine the historical trajectory of the U.S.-Mexico border and the reasons behind its geographic transformation.
- Students will be introduced to the principles of “distant reading” and “close reading” (textual analysis) methods.
- Students will learn how to use Voyant-Tools, a free web-based text visualization tool to 1.) identify common themes in the treaty and 2.) analyze the usage, definition, and significance of specific terms in the treaty’s political discourse.
- Students will learn how to examine the visual and textual information conveyed in maps to understand the historical events that influenced the positioning of the U.S.-Mexico border.
Relevant Teaching Standards
TEKS Guidelines
- Ethic Studies: Mexican American Studies
- (c)-(3)-(A) – Explain the significance of the following events as turning points relevant to Mexican American history: the Grito de Dolores, Mexico’s acquisition of independence, Texas’s declaration of independence from Mexico, Mexican-American War, Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, Mexican Revolution, creation of the U.S. Border Patrol, and Mexican repatriation of the 1930s
- World Geography Studies
- (c)-(1)-(B) – Trace the spatial diffusion of phenomena such as the Columbian Exchange or the diffusion of American popular culture and describe the effects on regions of contact.
- (c)-(13)-(A) – Interpret maps to explain the division of land, including man-made and natural borders, into separate political units such as cities, states, or countries; and
C3 Framework
- History
- D2.His.2.9-12. Analyze change and continuity in historical eras.
- D2.His.5.9-12. Analyze how historical contexts shaped and continue to shape people’s perspectives.
- D2.His.14.9-12. Analyze multiple and complex causes and effects of events in the past.
- Geography
- D2.Geo.2.9-12. Use maps, satellite images, photographs, and other representations to explain relationships between the locations of places and regions and their political, cultural, and economic dynamics.
- D2.Geo.7.9-12. Analyze the reciprocal nature of how historical events and the spatial diffusion of ideas, technologies, and cultural practices have influenced migration patterns and the distribution of human population.
Downloads
Assignment: PDF | Microsoft Word
“Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo” Texts for Voyant-Tools
Rights Statement
Creator(s): Alexandrea Noel Perez Allison, Doctoral Student, Department of English; & Albert A. Palacios, Digital Scholarship Coordinator, LLILAS Benson Latin American Studies and Collections
Date: 2019-08-21
This assignment is under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International Public License (“Public License”). This license lets others share, remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as they credit the creators and license their new creations under the identical terms.
